Embark on an intellectual odyssey with the diffusion and osmosis crossword puzzle answer key, an indispensable tool for deciphering the enigmatic realm of passive transport. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of diffusion and osmosis, providing a profound understanding of their fundamental principles and practical applications.
Prepare to delve into a labyrinth of clues that challenge your knowledge of key concepts, including the distinction between diffusion and osmosis, the factors influencing their rates, and their pivotal roles in biological systems. Immerse yourself in a narrative that illuminates the practical applications of diffusion and osmosis in diverse fields, from medicine to environmental science.
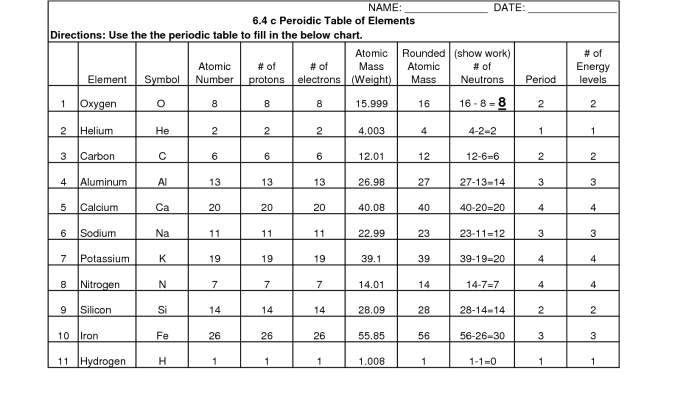
Diffusion and Osmosis: Definitions and Concepts
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental processes that govern the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable membrane. Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the specific movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.The
key difference between diffusion and osmosis lies in the nature of the molecules being transported. Diffusion involves the movement of any type of molecule, including gases, liquids, and solids, whereas osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules.
Factors Affecting Diffusion and Osmosis
The rate of diffusion and osmosis is influenced by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster diffusion and osmosis.
- Concentration gradient:The greater the difference in concentration between two areas, the faster the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
- Surface area:A larger surface area allows for more molecules to pass through the membrane, increasing the rate of diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion and Osmosis in Biological Systems
Diffusion and osmosis play crucial roles in various biological processes, including:
- Nutrient transport:Diffusion allows nutrients to move from areas of high concentration (e.g., the bloodstream) to areas of low concentration (e.g., cells).
- Waste removal:Diffusion facilitates the removal of waste products from cells to areas of lower concentration (e.g., the bloodstream).
- Cell function:Osmosis helps maintain cell volume and turgor pressure, which is essential for proper cell function.
Applications of Diffusion and Osmosis: Diffusion And Osmosis Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
Diffusion and osmosis have numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Medical treatments:Dialysis utilizes osmosis to remove waste products from the blood of patients with kidney failure.
- Industrial processes:Reverse osmosis is used to purify water and remove contaminants.
- Environmental science:Osmosis plays a role in the movement of water and nutrients in ecosystems.
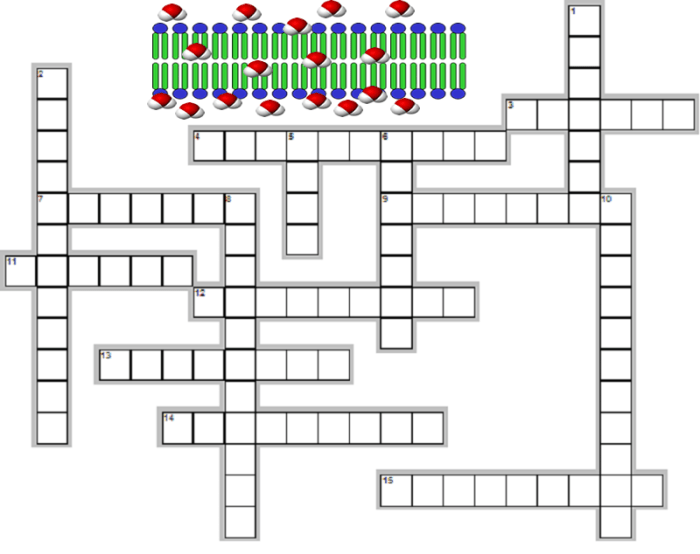
Diffusion and Osmosis Crossword Puzzle
Across
- The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration (7 letters)
- The movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane (6 letters)
- The difference in concentration between two areas (14 letters)
Down
- A factor that affects the rate of diffusion and osmosis (9 letters)
- A membrane that allows certain molecules to pass through (15 letters)
- The process of removing waste products from the blood using osmosis (7 letters)
Question Bank
What is the primary distinction between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion involves the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
As temperature increases, the kinetic energy of molecules increases, leading to a faster rate of diffusion.
Provide an example of osmosis in a biological system.
The absorption of water by plant roots is a classic example of osmosis, where water moves from the soil (low solute concentration) into the root cells (high solute concentration) through a semipermeable membrane.